Diabetic Eye Exam
“Diabetes is the single largest cause of blindness in Canada.”
A diabetic eye exam is crucial for diabetes management because it can detect early signs of eye disease, preventing vision loss and ensuring overall health.
Importance of Diabetic Eye Exams
- Early Detection: Many eye conditions caused by diabetes have no early symptoms. Regular exams can catch
issues before they become serious. - Prevent Vision Loss: Timely treatment can prevent or delay the progression of vision loss.
- Personalized Care: Your optometrist can tailor care based on your specific needs and diabetes management.
When should you book an exam?
Diabetic Eye Exam: Recommended frequency
- An annual eye exam is recommended unless your optometrist advises otherwise.
- Promptly visit your eye doctor if you notice sudden changes in your vision.
Keep in mind you may not notice changes occurring to your vision.
What to expect
Wondering what happens during a diabetic eye exam? Here’s aquick rundown:
- Dilation: Your eyes will be dilated to allow a thorough examination of your retina and optic nerve.
- Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques, like optical coherence tomography (OCT), provide detailed images of your eye's structure.
- Visual Acuity Test: This checks how well you see at various distances.
- Discussion: We’ll talk about your diabetes management and its impact on your vision.
Diabetes Eye Disease
These are serious complications of diabetes that can lead to vision loss, if left untreated.
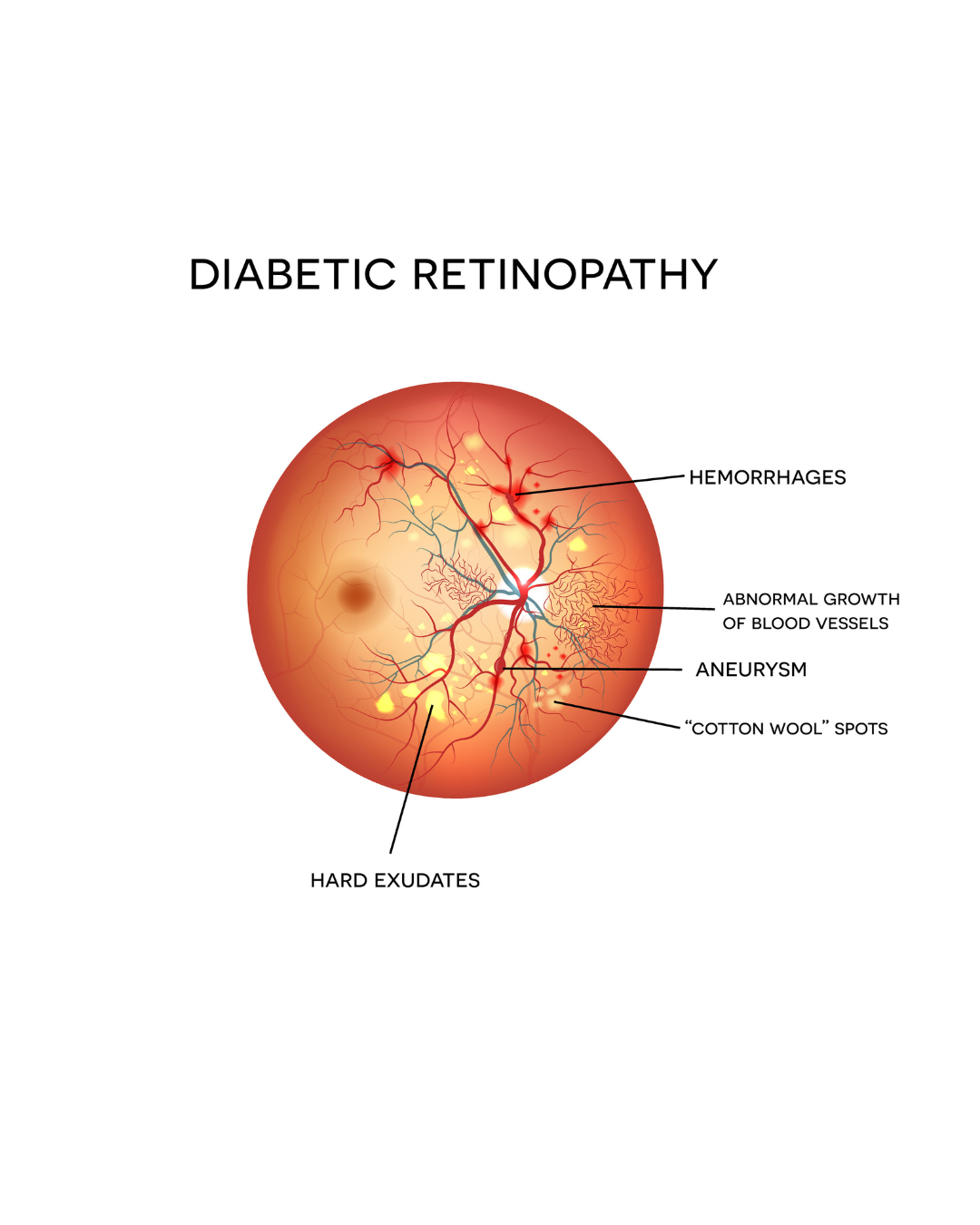
1. Diabetic Retinopathy:
- What it is: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina. It is one of the leading causes of blindness in Canada.
- Symptoms: Loss of central vision, blurred vision, flashes of light in field of vision, inability to see colours, black spots or holes in vision.
- Risk: Can lead to blindness if untreated.
2. Cataracts
- What it is: Clouding of the eye’s lens.
- Symptoms: Foggy vision, trouble seeing at night.
- Risk: People with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts at a younger age.
3. Glaucoma
- What it is: Increased pressure in the eye, damaging the optic nerve.
- Symptoms: Peripheral vision loss, halos around lights.
- Risk: Diabetics are at a higher risk
Retinopathy
Who should be screened and how often.
- Type 1 Diabetes Individuals over 15: It's essential to undergo annual screenings
starting five years after diabetes onset. - Type 2 Diabetes Individuals: Screening is crucial at the time of diagnosis and then every 1-2 years thereafter. Regular monitoring ensures timely intervention and prevents vision loss.
- Women with Diabetes or Planning Pregnancy: Screenings are recommended before conception, during the first trimester, as needed during pregnancy, and within the first year postpartum.
- Early detection is key to managing diabetic retinopathy effectively.
Schedule Your Screening Today.
Managing Diabetes
“Eye exams are part of managing your diabetes. Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can reduce the risk of blindness by 95 %.”
- National Eye Institute
Book an Appointment
Please note, not all optometrists are available through online booking - for more details, please call or email.
